Числа Фибоначчи — это числа в следующей целочисленной последовательности.
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, ……..
В математических терминах последовательность Fn чисел Фибоначчи определяется рекуррентным соотношением
Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2с начальными значениями
F0 = 0 и F1 = 1.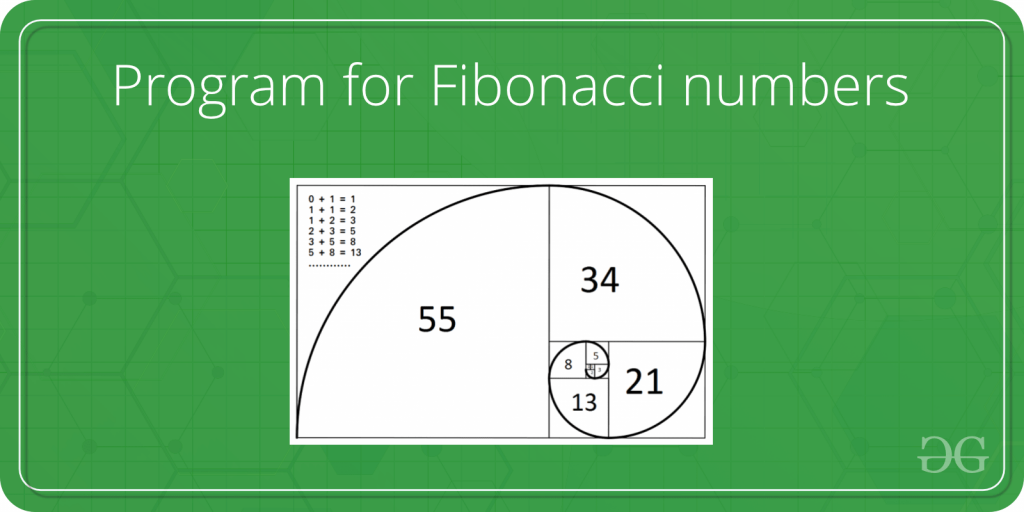
Учитывая число n, выведите n-е число Фибоначчи.
Примеры:
Вход : n = 2 Выход : 1 Вход : n = 9 Выход : 34
Напишите функцию int fib(int n), которая возвращает Fn. Например, если n = 0, то функция fib() должна возвращать 0. Если n = 1, то он должен возвращать 1. Для n > 1 он должен возвращать F>n-1 + Fn-2
Для n = 9 Выход:34
Ниже приведены различные методы получения n-го числа Фибоначчи.
Метод 1 (Используйте рекурсию)
Простой метод, представляющий собой прямую рекурсивную реализацию математического рекуррентного соотношения, приведенного выше.
C++//Fibonacci Series using Recursion #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int fib(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); } int main () { int n = 9; cout << fib(n); getchar(); return 0; } // This code is contributed // by Akanksha Rai
C//Fibonacci Series using Recursion #include<stdio.h> int fib(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); } int main () { int n = 9; printf("%d", fib(n)); getchar(); return 0; }
Java//Fibonacci Series using Recursion class fibonacci { static int fib(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); } public static void main (String args[]) { int n = 9; System.out.println(fib(n)); } } /* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
Python# Function for nth Fibonacci number def fib(n,st,en): if n-1==0: return enPytho if n>0: temp_st=en en=st+en return fib(n-1,temp_st,en) if __name__ == "__main__": print(fib(9,0,1)) #This code is contributed by Bhawna Priya
C#// C# program for Fibonacci Series // using Recursion using System; public class GFG { public static int Fib(int n) { if (n <= 1) { return n; } else { return Fib(n - 1) + Fib(n - 2); } } // driver code public static void Main(string[] args) { int n = 9; Console.Write(Fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Sam007
PHP<?php // Fibonacci Series // using Recursion // function returns // the Fibonacci number function fib($n) { if ($n <= 1) return $n; return fib($n - 1) + fib($n - 2); } // Driver Code $n = 9; echo fib($n); // This code is contributed by aj_36 ?>
JavaScript<script> //Fibonacci Series using Recursion let n = 9; // function returns the Fibonacci number function fib(n) { if (n <= 1) return n; return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); } //function call document.write(fib(n)); //This code is contributed by Surbhi Tyagi </script>
Выход:
34Временная сложность:T(n) = T(n) , которая является линейной.
Если бы исходное дерево рекурсии должно было быть реализовано, то это было бы дерево, но теперь в n раз вызывается функция рекурсии
Исходное дерево для рекурсии
fib(5) / \ fib(4) fib(3) / \ / \ fib(3) fib(2) fib(2) fib(1) / \ / \ / \ fib(2) fib(1) fib(1) fib(0) fib(1) fib(0) / \ fib(1) fib(0)
Оптимизированное дерево для рекурсии для кода выше
fib(5)
fib(4)
fib(3)
fib(2)
fib(1)
Дополнительное Пространство: O(n), если мы учитываем размер стека вызовов функций, в противном случае O(1).
Метод 2 (Используйте Динамическое программирование)
Мы можем избежать повторной работы, проделанной в методе 1, сохранив числа Фибоначчи, вычисленные до сих пор.
C++// C++ program for Fibonacci Series // using Dynamic Programming #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class GFG{ public: int fib(int n) { // Declare an array to store // Fibonacci numbers. // 1 extra to handle // case, n = 0 int f[n + 2]; int i; // 0th and 1st number of the // series are 0 and 1 f[0] = 0; f[1] = 1; for(i = 2; i <= n; i++) { //Add the previous 2 numbers // in the series and store it f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2]; } return f[n]; } }; // Driver code int main () { GFG g; int n = 9; cout << g.fib(n); return 0; } // This code is contributed by SoumikMondal
C//Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming #include<stdio.h> int fib(int n) { /* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */ int f[n+2]; // 1 extra to handle case, n = 0 int i; /* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/ f[0] = 0; f[1] = 1; for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) { /* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series and store it */ f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2]; } return f[n]; } int main () { int n = 9; printf("%d", fib(n)); getchar(); return 0; }
Java// Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming class fibonacci { static int fib(int n) { /* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */ int f[] = new int[n+2]; // 1 extra to handle case, n = 0 int i; /* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/ f[0] = 0; f[1] = 1; for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) { /* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series and store it */ f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2]; } return f[n]; } public static void main (String args[]) { int n = 9; System.out.println(fib(n)); } } /* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
Python# Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming def fibonacci(n): # Taking 1st two fibonacci numbers as 0 and 1 f = [0, 1] for i in range(2, n+1): f.append(f[i-1] + f[i-2]) return f[n] print(fibonacci(9))
C#// C# program for Fibonacci Series // using Dynamic Programming using System; class fibonacci { static int fib(int n) { // Declare an array to // store Fibonacci numbers. // 1 extra to handle // case, n = 0 int []f = new int[n + 2]; int i; /* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1 */ f[0] = 0; f[1] = 1; for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) { /* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series and store it */ f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2]; } return f[n]; } // Driver Code public static void Main () { int n = 9; Console.WriteLine(fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed by anuj_67.
PHP<?php //Fibonacci Series using Dynamic // Programming function fib( $n) { /* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */ // 1 extra to handle case, // n = 0 $f = array(); $i; /* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/ $f[0] = 0; $f[1] = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <= $n; $i++) { /* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series and store it */ $f[$i] = $f[$i-1] + $f[$i-2]; } return $f[$n]; } $n = 9; echo fib($n); // This code is contributed by // anuj_67. ?>
JavaSpript<script> // Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming function fib(n) { /* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */ let f = new Array(n+2); // 1 extra to handle case, n = 0 let i; /* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/ f[0] = 0; f[1] = 1; for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) { /* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series and store it */ f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2]; } return f[n]; } let n=9; document.write(fib(n)); // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 </script>
Выход:
34Метод 3 (Метод 2, оптимизированный для пространства)
Мы можем оптимизировать пространство, используемое в методе 2, сохранив два предыдущих числа только потому, что это все, что нам нужно, чтобы последовательно получить следующее число Фибоначчи.
C++// Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int fib(int n) { int a = 0, b = 1, c, i; if( n == 0) return a; for(i = 2; i <= n; i++) { c = a + b; a = b; b = c; } return b; } // Driver code int main() { int n = 9; cout << fib(n); return 0; } // This code is contributed by Code_Mech
C// Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method #include<stdio.h> int fib(int n) { int a = 0, b = 1, c, i; if( n == 0) return a; for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) { c = a + b; a = b; b = c; } return b; } int main () { int n = 9; printf("%d", fib(n)); getchar(); return 0; }
Java// Java program for Fibonacci Series using Space // Optimized Method class fibonacci { static int fib(int n) { int a = 0, b = 1, c; if (n == 0) return a; for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { c = a + b; a = b; b = c; } return b; } public static void main (String args[]) { int n = 9; System.out.println(fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Mihir Joshi
Python# Function for nth fibonacci number - Space Optimisation # Taking 1st two fibonacci numbers as 0 and 1 def fibonacci(n): a = 0 b = 1 if n < 0: print("Incorrect input") elif n == 0: return a elif n == 1: return b else: for i in range(2,n+1): c = a + b a = b b = c return b # Driver Program print(fibonacci(9)) #This code is contributed by Saket Modi
C#// C# program for Fibonacci Series // using Space Optimized Method using System; namespace Fib { public class GFG { static int Fib(int n) { int a = 0, b = 1, c = 0; // To return the first Fibonacci number if (n == 0) return a; for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { c = a + b; a = b; b = c; } return b; } // Driver function public static void Main(string[] args) { int n = 9; Console.Write("{0} ", Fib(n)); } } } // This code is contributed by Sam007.
PHP<?php // PHP program for Fibonacci Series // using Space Optimized Method function fib( $n) { $a = 0; $b = 1; $c; $i; if( $n == 0) return $a; for($i = 2; $i <= $n; $i++) { $c = $a + $b; $a = $b; $b = $c; } return $b; } // Driver Code $n = 9; echo fib($n); // This code is contributed by anuj_67. ?>
JavaSpript<script> // Javascript program for Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method function fib(n) { let a = 0, b = 1, c, i; if( n == 0) return a; for(i = 2; i <= n; i++) { c = a + b; a = b; b = c; } return b; } // Driver code let n = 9; document.write(fib(n)); // This code is contributed by Mayank Tyagi </script>
Выход:
34Временная сложность: O(n)
Дополнительное пространство: O(1)
Метод 4 (использование мощности матрицы {{1, 1}, {1, 0}})
это еще порядка O(N), которое полагается на то, что если мы N раз умножить матрицу м = {{1,1},{1,0}} для себя (другими словами рассчитать мощность(М, N)), тогда мы получим (П+1) — му числу Фибоначчи как элемент в строке и столбце (0, 0) в результирующей матрицы.
Представленность матрицы дает следующие закрытые выражение для чисел Фибоначчи :
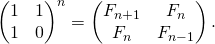
C++#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Helper function that multiplies 2 // matrices F and M of size 2*2, and // puts the multiplication result // back to F[][] void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]); // Helper function that calculates F[][] // raise to the power n and puts the // result in F[][] // Note that this function is designed // only for fib() and won't work as // general power function void power(int F[2][2], int n); int fib(int n) { int F[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } }; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n - 1); return F[0][0]; } void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]) { int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0]; int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1]; int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0]; int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1]; F[0][0] = x; F[0][1] = y; F[1][0] = z; F[1][1] = w; } void power(int F[2][2], int n) { int i; int M[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } }; // n - 1 times multiply the // matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}} for(i = 2; i <= n; i++) multiply(F, M); } // Driver code int main() { int n = 9; cout << " " << fib(n); return 0; } // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C#include <stdio.h> /* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, and puts the multiplication result back to F[][] */ void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]); /* Helper function that calculates F[][] raise to the power n and puts the result in F[][] Note that this function is designed only for fib() and won't work as general power function */ void power(int F[2][2], int n); int fib(int n) { int F[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}}; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n-1); return F[0][0]; } void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]) { int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0]; int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1]; int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0]; int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1]; F[0][0] = x; F[0][1] = y; F[1][0] = z; F[1][1] = w; } void power(int F[2][2], int n) { int i; int M[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}}; // n - 1 times multiply the matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}} for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) multiply(F, M); } /* Driver program to test above function */ int main() { int n = 9; printf("%d", fib(n)); getchar(); return 0; }
Javaclass fibonacci { static int fib(int n) { int F[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}}; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n-1); return F[0][0]; } /* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, and puts the multiplication result back to F[][] */ static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][]) { int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0]; int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1]; int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0]; int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1]; F[0][0] = x; F[0][1] = y; F[1][0] = z; F[1][1] = w; } /* Helper function that calculates F[][] raise to the power n and puts the result in F[][] Note that this function is designed only for fib() and won't work as general power function */ static void power(int F[][], int n) { int i; int M[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}}; // n - 1 times multiply the matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}} for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) multiply(F, M); } /* Driver program to test above function */ public static void main (String args[]) { int n = 9; System.out.println(fib(n)); } } /* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
Python# Helper function that multiplies # 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, # and puts the multiplication # result back to F[][] # Helper function that calculates # F[][] raise to the power n and # puts the result in F[][] # Note that this function is # designed only for fib() and # won't work as general # power function def fib(n): F = [[1, 1], [1, 0]] if (n == 0): return 0 power(F, n - 1) return F[0][0] def multiply(F, M): x = (F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0]) y = (F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1]) z = (F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0]) w = (F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1]) F[0][0] = x F[0][1] = y F[1][0] = z F[1][1] = w def power(F, n): M = [[1, 1], [1, 0]] # n - 1 times multiply the # matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}} for i in range(2, n + 1): multiply(F, M) # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": n = 9 print(fib(n)) # This code is contributed # by ChitraNayal
C#using System; class GFG { static int fib(int n) { int [,]F = new int[,] {{1, 1}, {1, 0} }; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n-1); return F[0,0]; } /* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, and puts the multiplication result back to F[][] */ static void multiply(int [,]F, int [,]M) { int x = F[0,0]*M[0,0] + F[0,1]*M[1,0]; int y = F[0,0]*M[0,1] + F[0,1]*M[1,1]; int z = F[1,0]*M[0,0] + F[1,1]*M[1,0]; int w = F[1,0]*M[0,1] + F[1,1]*M[1,1]; F[0,0] = x; F[0,1] = y; F[1,0] = z; F[1,1] = w; } /* Helper function that calculates F[][] raise to the power n and puts the result in F[][] Note that this function is designed only for fib() and won't work as general power function */ static void power(int [,]F, int n) { int i; int [,]M = new int[,]{{1, 1}, {1, 0} }; // n - 1 times multiply the matrix to // {{1,0},{0,1}} for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) multiply(F, M); } /* Driver program to test above function */ public static void Main () { int n = 9; Console.WriteLine(fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed by anuj_67.
PHP<?php function fib($n) { $F = array(array(1, 1), array(1, 0)); if ($n == 0) return 0; power($F, $n - 1); return $F[0][0]; } function multiply(&$F, &$M) { $x = $F[0][0] * $M[0][0] + $F[0][1] * $M[1][0]; $y = $F[0][0] * $M[0][1] + $F[0][1] * $M[1][1]; $z = $F[1][0] * $M[0][0] + $F[1][1] * $M[1][0]; $w = $F[1][0] * $M[0][1] + $F[1][1] * $M[1][1]; $F[0][0] = $x; $F[0][1] = $y; $F[1][0] = $z; $F[1][1] = $w; } function power(&$F, $n) { $M = array(array(1, 1), array(1, 0)); // n - 1 times multiply the // matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}} for ($i = 2; $i <= $n; $i++) multiply($F, $M); } // Driver Code $n = 9; echo fib($n); // This code is contributed // by ChitraNayal ?>
JavaSpript<script> // Note that this function is designed // only for fib() and won't work as // general power function function fib( n) { var F = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ]; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n - 1); return F[0][0]; } // Helper function that multiplies 2 // matrices F and M of size 2*2, and // puts the multiplication result // back to F[][] function multiply( F, M ) { x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0]; y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1]; z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0]; w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1]; F[0][0] = x; F[0][1] = y; F[1][0] = z; F[1][1] = w; } // Helper function that calculates F[][] // raise to the power n and puts the // result in F[][] function power( F, n) { var i; var M = [[ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ]]; // n - 1 times multiply the // matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}} for(i = 2; i <= n; i++) multiply(F, M); } // Driver code var n = 9; document.write (" " + fib(n)); //This code is contributed by sweetyty </script>
Выход:
34Временная сложность: O(n)
Дополнительное пространство: O(1)
Метод 5 (Оптимизированный метод 4)
Метод 4 может быть оптимизирован для работы в O(логарифмической) временной сложности. Мы можем выполнить рекурсивное умножение, чтобы получить мощность(M, n) в предыдущем методе.
C++// Fibonacci Series using Optimized Method #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]); void power(int F[2][2], int n); // Function that returns nth Fibonacci number int fib(int n) { int F[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}}; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n - 1); return F[0][0]; } // Optimized version of power() in method 4 void power(int F[2][2], int n) { if(n == 0 || n == 1) return; int M[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}}; power(F, n / 2); multiply(F, F); if (n % 2 != 0) multiply(F, M); } void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]) { int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0]; int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1]; int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0]; int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1]; F[0][0] = x; F[0][1] = y; F[1][0] = z; F[1][1] = w; } // Driver code int main() { int n = 9; cout << fib(9); getchar(); return 0; } // This code is contributed by Nidhi_biet
C#include <stdio.h> void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]); void power(int F[2][2], int n); /* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */ int fib(int n) { int F[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}}; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n-1); return F[0][0]; } /* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */ void power(int F[2][2], int n) { if( n == 0 || n == 1) return; int M[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}}; power(F, n/2); multiply(F, F); if (n%2 != 0) multiply(F, M); } void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]) { int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0]; int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1]; int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0]; int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1]; F[0][0] = x; F[0][1] = y; F[1][0] = z; F[1][1] = w; } /* Driver program to test above function */ int main() { int n = 9; printf("%d", fib(9)); getchar(); return 0; }
Java//Fibonacci Series using Optimized Method class fibonacci { /* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */ static int fib(int n) { int F[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}}; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n-1); return F[0][0]; } static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][]) { int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0]; int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1]; int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0]; int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1]; F[0][0] = x; F[0][1] = y; F[1][0] = z; F[1][1] = w; } /* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */ static void power(int F[][], int n) { if( n == 0 || n == 1) return; int M[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}}; power(F, n/2); multiply(F, F); if (n%2 != 0) multiply(F, M); } /* Driver program to test above function */ public static void main (String args[]) { int n = 9; System.out.println(fib(n)); } } /* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
Python# Fibonacci Series using # Optimized Method # function that returns nth # Fibonacci number def fib(n): F = [[1, 1], [1, 0]] if (n == 0): return 0 power(F, n - 1) return F[0][0] def multiply(F, M): x = (F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0]) y = (F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1]) z = (F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0]) w = (F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1]) F[0][0] = x F[0][1] = y F[1][0] = z F[1][1] = w # Optimized version of # power() in method 4 def power(F, n): if( n == 0 or n == 1): return; M = [[1, 1], [1, 0]]; power(F, n // 2) multiply(F, F) if (n % 2 != 0): multiply(F, M) # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": n = 9 print(fib(n)) # This code is contributed # by ChitraNayal
C#// Fibonacci Series using // Optimized Method using System; class GFG { /* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */ static int fib(int n) { int[,] F = new int[,]{{1, 1}, {1, 0}}; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n - 1); return F[0, 0]; } static void multiply(int[,] F, int[,] M) { int x = F[0, 0] * M[0, 0] + F[0, 1] * M[1, 0]; int y = F[0, 0] * M[0, 1] + F[0, 1] * M[1, 1]; int z = F[1, 0] * M[0, 0] + F[1, 1] * M[1, 0]; int w = F[1, 0] * M[0, 1] + F[1, 1] * M[1, 1]; F[0, 0] = x; F[0, 1] = y; F[1, 0] = z; F[1, 1] = w; } /* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */ static void power(int[,] F, int n) { if( n == 0 || n == 1) return; int[,] M = new int[,]{{1, 1}, {1, 0}}; power(F, n / 2); multiply(F, F); if (n % 2 != 0) multiply(F, M); } // Driver Code public static void Main () { int n = 9; Console.Write(fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by ChitraNayal
JavaSpript<script> // Fibonacci Series using Optimized Method // Function that returns nth Fibonacci number function fib(n) { var F = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ]; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n - 1); return F[0][0]; } function multiply(F, M) { var x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0]; var y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1]; var z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0]; var w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1]; F[0][0] = x; F[0][1] = y; F[1][0] = z; F[1][1] = w; } // Optimized version of power() in method 4 */ function power(F, n) { if (n == 0 || n == 1) return; var M = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ]; power(F, n / 2); multiply(F, F); if (n % 2 != 0) multiply(F, M); } // Driver code var n = 9; document.write(fib(n)); // This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 </script>
Выход:
Временная Сложность: O(Логин)
Дополнительное Пространство: O(Logn), если мы учитываем размер стека вызовов функций, в противном случае O(1).
Способ 6 (O(Log n) Время)
Ниже приведена еще одна интересная рекуррентная формула, которую можно использовать для нахождения n-го числа Фибоначчи за O(Log n) времени.
If n is even then k = n/2:
F(n) = [2*F(k-1) + F(k)]*F(k)
If n is odd then k = (n + 1)/2
F(n) = F(k)*F(k) + F(k-1)*F(k-1)Как работает эта формула?
Формула может быть получена из приведенного выше матричного уравнения.
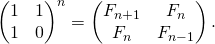
Принимая определитель с обеих сторон, мы получаем
(-1)n = Fn+1Fn-1 - Fn2
Более того, поскольку AnAm = An+m для любой квадратной матрицы A,
могут быть получены следующие тождества (они получены
из двух разных коэффициентов матричного произведения)
FmFn + Fm-1Fn-1 = Fm+n-1 ---------------------------(1)
Поместив n = n+1 в уравнение(1),
FmFn+1 + Fm-1Fn = Fm+n --------------------------(2)
Введем m = n в уравнение(1).
F2n-1 = Fn2 + Fn-12
Включение m = n в уравнение(2)
F2n = (Fn-1 + Fn+1)Fn = (2Fn-1 + Fn)Fn (Источник: Wiki) --------
( Поставив Fn+1 = Fn + Fn-1 )
Чтобы доказать формулу, нам просто нужно сделать следующее
Если n четное, мы можем положить k = n/2
Если n нечетно, мы можем положить k = (n+1)/2Ниже приведена реализация вышеуказанной идеи.
C++// C++ Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in // with O(Log n) arithmetic operations #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int MAX = 1000; // Create an array for memoization int f[MAX] = {0}; // Returns n'th fibonacci number using table f[] int fib(int n) { // Base cases if (n == 0) return 0; if (n == 1 || n == 2) return (f[n] = 1); // If fib(n) is already computed if (f[n]) return f[n]; int k = (n & 1)? (n+1)/2 : n/2; // Applying above formula [Note value n&1 is 1 // if n is odd, else 0. f[n] = (n & 1)? (fib(k)*fib(k) + fib(k-1)*fib(k-1)) : (2*fib(k-1) + fib(k))*fib(k); return f[n]; } /* Driver program to test above function */ int main() { int n = 9; printf("%d ", fib(n)); return 0; }
Java// Java Program to find n'th fibonacci // Number with O(Log n) arithmetic operations import java.util.*; class GFG { static int MAX = 1000; static int f[]; // Returns n'th fibonacci number using // table f[] public static int fib(int n) { // Base cases if (n == 0) return 0; if (n == 1 || n == 2) return (f[n] = 1); // If fib(n) is already computed if (f[n] != 0) return f[n]; int k = (n & 1) == 1? (n + 1) / 2 : n / 2; // Applying above formula [Note value // n&1 is 1 if n is odd, else 0. f[n] = (n & 1) == 1? (fib(k) * fib(k) + fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1)) : (2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k)) * fib(k); return f[n]; } /* Driver program to test above function */ public static void main(String[] args) { int n = 9; f= new int[MAX]; System.out.println(fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal.
Python# Python3 Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in # with O(Log n) arithmetic operations MAX = 1000 # Create an array for memoization f = [0] * MAX # Returns n'th fibonacci number using table f[] def fib(n) : # Base cases if (n == 0) : return 0 if (n == 1 or n == 2) : f[n] = 1 return (f[n]) # If fib(n) is already computed if (f[n]) : return f[n] if( n & 1) : k = (n + 1) // 2 else : k = n // 2 # Applying above formula [Note value n&1 is 1 # if n is odd, else 0. if((n & 1) ) : f[n] = (fib(k) * fib(k) + fib(k-1) * fib(k-1)) else : f[n] = (2*fib(k-1) + fib(k))*fib(k) return f[n] # Driver code n = 9 print(fib(n)) # This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
C#// C# Program to find n'th // fibonacci Number with // O(Log n) arithmetic operations using System; class GFG { static int MAX = 1000; static int[] f; // Returns n'th fibonacci // number using table f[] public static int fib(int n) { // Base cases if (n == 0) return 0; if (n == 1 || n == 2) return (f[n] = 1); // If fib(n) is already // computed if (f[n] != 0) return f[n]; int k = (n & 1) == 1 ? (n + 1) / 2 : n / 2; // Applying above formula // [Note value n&1 is 1 if // n is odd, else 0. f[n] = (n & 1) == 1 ? (fib(k) * fib(k) + fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1)) : (2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k)) * fib(k); return f[n]; } // Driver Code static void Main() { int n = 9; f = new int[MAX]; Console.WriteLine(fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed by mits
PHP<?php // PHP Program to find n'th // fibonacci Number in with // O(Log n) arithmetic operations $MAX = 1000; // Returns n'th fibonacci // number using table f[] function fib($n) { global $MAX; // Create an array for memoization $f = array_fill(0, $MAX, NULL); // Base cases if ($n == 0) return 0; if ($n == 1 || $n == 2) return ($f[$n] = 1); // If fib(n) is already computed if ($f[$n]) return $f[$n]; $k = ($n & 1) ? ($n + 1) / 2 : $n / 2; // Applying above formula // [Note value n&1 is 1 if // n is odd, else 0. $f[$n] = ($n & 1) ? (fib($k) * fib($k) + fib($k - 1) * fib($k - 1)) : (2 * fib($k - 1) + fib($k)) * fib($k); return $f[$n]; } // Driver Code $n = 9; echo fib($n); // This code is contributed // by ChitraNayal ?>
JavaSpript<script> // JavaScript Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in // with O(Log n) arithmetic operations const MAX = 1000; // Create an array for memoization var f = [...Array(MAX)]; f.fill(0); // Returns n'th fibonacci number using table f[] function fib(n) { // Base cases if (n == 0) return 0; if (n == 1 || n == 2) return (f[n] = 1); // If fib(n) is already computed if (f[n]) return f[n]; var k = n & 1 ? (n + 1) / 2 : n / 2; // Applying above formula [Note value n&1 is 1 // if n is odd, else 0. f[n] = n & 1 ? fib(k) * fib(k) + fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1) : (2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k)) * fib(k); return f[n]; } /* Driver program to test above function */ var n = 9; document.write(fib(n)); // This code is contributed by rdtank. </script>
Выход:
34Временная сложность этого решения равна O(Log n), так как мы разделяем проблему на две части в каждом рекурсивном вызове.
Способ 7
Другой подход(с использованием формулы) :
В этом методе мы непосредственно реализуем формулу для n-го члена в ряду Фибоначчи.
Fn = {[(√5 + 1)/2] ^ n} / √5
C++// C++ Program to find n'th fibonacci Number #include<iostream> #include<cmath> int fib(int n) { double phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2; return round(pow(phi, n) / sqrt(5)); } // Driver Code int main () { int n = 9; std::cout << fib(n) << std::endl; return 0; } //This code is contributed by Lokesh Mohanty.
C// C Program to find n'th fibonacci Number #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> int fib(int n) { double phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2; return round(pow(phi, n) / sqrt(5)); } int main () { int n = 9; printf("%d", fib(n)); return 0; }
Java// Java Program to find n'th fibonacci Number import java.util.*; class GFG { static int fib(int n) { double phi = (1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2; return (int) Math.round(Math.pow(phi, n) / Math.sqrt(5)); } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { int n = 9; System.out.println(fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Python# Python3 program to find n'th # fibonacci Number import math def fibo(n): phi = (1 + math.sqrt(5)) / 2 return round(pow(phi, n) / math.sqrt(5)) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': n = 9 print(fibo(n)) # This code is contributed by prasun_parate
C#// C# Program to find n'th fibonacci Number using System; public class GFG { static int fib(int n) { double phi = (1 + Math.Sqrt(5)) / 2; return (int) Math.Round(Math.Pow(phi, n) / Math.Sqrt(5)); } // Driver code public static void Main() { int n = 9; Console.WriteLine(fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
PHP<?php // PHP Program to find n'th // fibonacci Number function fib($n) { $phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2; return round(pow($phi, $n) / sqrt(5)); } // Driver Code $n = 9; echo fib($n) ; // This code is contributed by Ryuga ?>
JavaSpript<script> // Javascript Program to find n'th fibonacci Number function fib(n) { let phi = (1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2; return Math.round(Math.pow(phi, n) / Math.sqrt(5)); } let n = 9; document.write(fib(n)); // This code is contributed by mukesh07. </script>
Выход:
34Временная сложность: O(logn), это связано с тем, что для вычисления phi^n требуется
логарифмическая сложность временного пространства: O(1)
Способ 8
DP с использованием запоминания(подход сверху вниз)
Мы можем избежать повторной работы, проделанной методом 1, сохранив числа Фибоначчи, вычисленные до сих пор. Нам просто нужно сохранить все значения в массиве.
C++#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int dp[10]; int fib(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; // temporary variables to store // values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2) int first, second; if (dp[n - 1] != -1) first = dp[n - 1]; else first = fib(n - 1); if (dp[n - 2] != -1) second = dp[n - 2]; else second = fib(n - 2); // memoization return dp[n] = first + second; } // Driver Code int main() { int n = 9; memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp)); cout << fib(n); getchar(); return 0; // This code is contributed by Bhavneet Singh }
Javaimport java.util.*; class GFG{ // Initialize array of dp static int[] dp = new int[10]; static int fib(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; // Temporary variables to store // values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2) int first, second; if (dp[n - 1] != -1) first = dp[n - 1]; else first = fib(n - 1); if (dp[n - 2] != -1) second = dp[n - 2]; else second = fib(n - 2); // Memoization return dp[n] = first + second; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { int n = 9; Arrays.fill(dp, -1); System.out.print(fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sujitmeshram
Python# Initialize array of dp dp = [-1 for i in range(10)] def fib(n): if (n <= 1): return n; global dp; # Temporary variables to store # values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2) first = 0; second = 0; if (dp[n - 1] != -1): first = dp[n - 1]; else: first = fib(n - 1); if (dp[n - 2] != -1): second = dp[n - 2]; else: second = fib(n - 2); dp[n] = first + second; # Memoization return dp[n] ; # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': n = 9; print(fib(n)); # This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
C#using System; class GFG { // Initialize array of dp static int[] dp = new int[10]; static int fib(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; // Temporary variables to store // values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2) int first, second; if (dp[n - 1] != -1) first = dp[n - 1]; else first = fib(n - 1); if (dp[n - 2] != -1) second = dp[n - 2]; else second = fib(n - 2); // Memoization return dp[n] = first + second; } // Driver code static void Main() { int n = 9; Array.Fill(dp, -1); Console.Write(fib(n)); } } // This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07.
JavaSpript<script> // Initialize array of dp dp = Array.from({length: 10}, (_, i) => -1); function fib(n) { if (n <= 1) return n; // Temporary variables to store // values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2) var first, second; if (dp[n - 1] != -1) first = dp[n - 1]; else first = fib(n - 1); if (dp[n - 2] != -1) second = dp[n - 2]; else second = fib(n - 2); // Memoization return dp[n] = first + second; } // Driver Code var n = 9; document.write(fib(n)); // This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar </script>
Выход:
34

